Accumulated depreciation is the most prevalent type of contra-asset account. It represents all the depreciation related to an asset or the company’s overall assets. Usually, companies add to the accumulated depreciation account after every accounting period.
Recording Contra Accounts
All three values can be useful for investors depending on what they’re looking for. Most accountants choose to record the depreciation over the useful life of an item in the accumulated depreciation contra asset account, which is a credit account. The balance sheet would show the piece of equipment at its historical cost, then subtract the accumulated depreciation to reflect the accurate value of the asset. They are also helpful for keeping the books balanced and creating a clear trail of financial breadcrumbs for historical review and reporting. For instance, it is common to keep the purchase price of a piece of equipment as a historical cost in the debit asset account when it comes to fixed assets. A contra liability is a general ledger account with a debit balance that reduces the normal credit balance of a standard liability account to present the net value on a balance sheet.
Do Contra Accounts Have Debit or Credit Balances?
- A contra account is used to show the opposite effect or reduction of a related account.
- In bookkeeping terms, a contra asset account refers to an account which is offset against an asset account.
- Contra liability accounts are mainly used by corporations that issue bonds frequently.
- The bond is listed on the balance sheet at the full amount of $1,000, but the cash received is just $950, so a contra liability for the discount is listed to make the entry balance.
Companies like to depreciate assets as quickly as possible to get the tax savings, so the balance sheet may not state the true value of fixed assets. A less common example of a contra asset account is Discount on Notes Receivable. The credit balance in this account is amortized or allocated to Interest Income or Interest Revenue over the life of a note receivable. While accumulated depreciation is the most common contra asset account, the following also may apply, depending on the company. A contra asset is a negative account used in double-entry accounting to reduce the balance of a paired asset account in the general ledger. In either case, using these accounts can help you better manage depreciation expense, keep your accounts receivable balance accurate, and properly dispose of and account for obsolete inventory.
What are the types of Contra Asset Accounts?
Home Depot reports net receivables and net property and equipment, implying that both are reduced by contra assets. We’ll need to dig into the footnotes to find out what the contra accounts are. The Notes Receivable account documents the total value of any promissory notes held by the company. Typically, these notes reflect purchases made on credit by your customers. To obtain a cash payout before the note reaches maturity, you can sell these notes to a bank or other financial institution for some price below the note’s face value.
What is a Contra Asset Account?
- Therefore, the book value of an asset in the books is equal to its historical cost (the debit balance of the asset) minus the related amount of contra asset in the balance sheet (the credit balance of the contra asset).
- Hence, the book value of the liability will be the credit balance of the liability account minus the debit balance of its contra liability counterpart.
- Learn why contra accounts, when utilized correctly along with a paired account, are a crucial component of accurate accounting and financial review.
- As you saw in the example, contra accounts can be an important part of your financial statement analysis, but they are hard to find.
- To oppose the revenue made by a company, contra revenue accounts must have a debit balance.
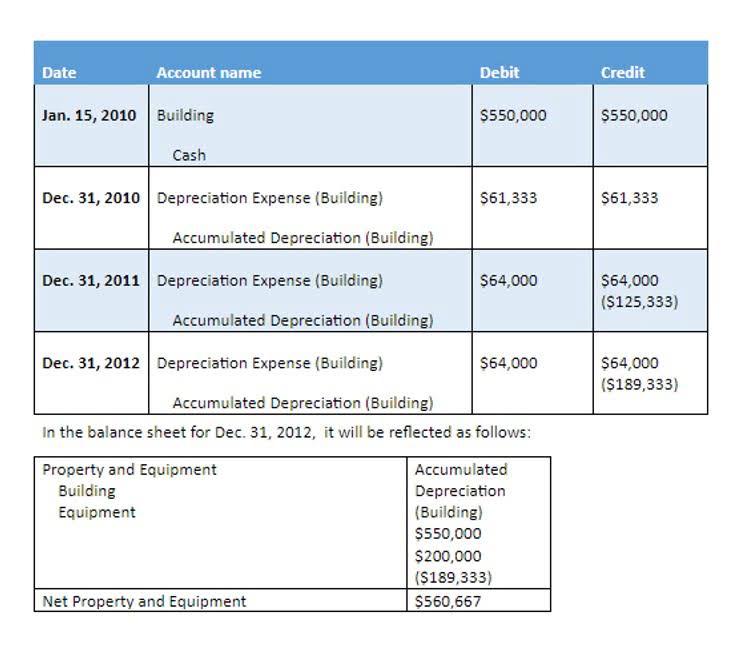
By doing so, they can bring their asset accounts to a more accurate position. Contra asset accounts are necessary for companies for various reasons. The most prominent of these include allowing companies to present a more accurate picture of their assets. For example, after six years, the asset’s book value on the balance sheet will be $40,000. However, it will also have a negative accumulated depreciation of $60,000, offsetting that cost.

Income Statement: Definition, Types, Templates, Examples, and More
In this way, the historical cost, the amount of write-off, and the book value of an asset can always be seen on the balance sheet. Similarly, it allows companies to retrieve original account balances without complicated calculations. For stakeholders, looking at both accounts is also crucial in their decision-making process. The accounting entries contra account for a discount on notes receivables are as follows. In footnote 3, the company reports, “Net property and equipment includes accumulated depreciation and amortization of $25.3 billion as of August 1, 2021 and $24.1 billion as of January 31, 2021.” In other words, contra revenue is a deduction from gross revenue, which results in net revenue.
This process will give rise to a contra asset account which is the discount on notes receivables. Instead, the existence of contra-asset accounts for companies will differ based on a company’s requirements. A contra-asset account is an account that opposes the balances of other asset accounts. As mentioned, a company will usually have debit balances in its asset accounts. As a reminder, assets and expenses are debit accounts whereas liabilities and revenues are credit accounts.
Example #1: Revenue Contra Account
- Contra Equity Account – A contra equity account has a debit balance and decreases a standard equity account.
- This make sense because Home Depot wouldn’t be carrying accounts receivable with long payment terms.
- If we record depreciation expense in the cost accounts directly, we will lose key information about the original cost of the assets and accumulated depreciation.
- This way the company can report an item on the balance sheet at itsoriginal amount and show a reduction in value separately in order to report itsnet realizable value.
- There are several examples of contra accounts, including accumulated depreciation, accumulated depletion, accumulated amortization, allowance for receivables, etc.
Contra liability accounts are less commonly used than contra asset accounts. Contra liability accounts are mainly used by corporations that issue bonds frequently. That is because some of the bonds are issued at a discount, so this reduces the balance of their bonds payable. However, the “Allowance for Doubtful Accounts” (or “Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts”) is a contra account related to the concept of bad debts. This contra-asset account reduces the accounts receivable balance on the balance sheet to its net realizable value. The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts carries a credit balance that reduces the total amount of accounts receivable to show the amount that the company expects to collect.
The most common contra equity account is called “treasury stock.” This special account decreases the number of shares outstanding in the market because the company repurchases some of the shares from its buyers. Therefore, it reduces the value of shareholders’ equity by the amount paid for those repurchased stocks. Sometimes, the current value of a note receivable will fall compared to its face value.